About the Problem of Climate Warming
Introduction
Climate change is a pivotal issue facing our planet, invoking wide-ranging studies and discussions on its causes, impacts, and solutions. In this comprehensive analysis, we delve into the historical data on climate warming, examining both natural and anthropogenic influences and discussing innovative strategies for mitigation.
Historical Context of Climate Warming
The article explores the warming patterns observed during the Holocene and contrasts these natural cycles with the recent trends attributed to human activities. It’s important to understand that climate has always been subject to changes; however, the rate and scale of recent temperature rises present unprecedented challenges.
Early Records and Natural Variability
Climate warming has been rigorously analyzed through data from meteorological stations worldwide, with records dating back to the 1800s. These long-term data sets reveal patterns of multi-decadal fluctuations and the roles of phenomena like the Little Ice Age, providing context for understanding current trends.
Twentieth Century Onset
It was around 1950 when anthropogenic factors began to significantly impact climate trends. The industrial activities of the modern era, marked by increased greenhouse gas emissions, have accelerated warming trends, making it a prominent issue of the last century.
Graphical Analysis of Climate Data
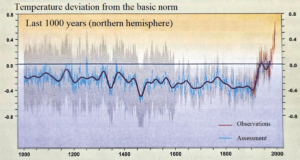 Figure 1: Changes in the average annual air temperature of the Northern Hemisphere [4].
Figure 1: Changes in the average annual air temperature of the Northern Hemisphere [4].
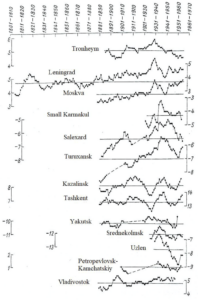 Figure 2: Moving 10-year average temperatures, years.
Figure 2: Moving 10-year average temperatures, years.
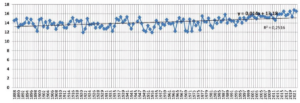 Figure 3: Average annual air temperature at the Tashkent observatory.
Figure 3: Average annual air temperature at the Tashkent observatory.
Anthropogenic Impacts and Global Response
The post-1950 era brought about a discernible shift in temperature trends, largely due to human activities. This section explores how industrialization, deforestation, and carbon emissions have contributed to climate warming, referencing current research and international climate summits.
Technological Innovations and Green Energy Advancements in solar and wind energy, biofuels, and other sustainable practices are highlighted as critical to mitigating climate impact. The role of new technologies in enhancing CO₂ sequestration and the potential of nuclear energy are discussed as part of a broader strategy to address global warming.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite significant research and technological advances, the battle against climate warming faces numerous obstacles. These include political, economic, and social barriers that hinder comprehensive global action. Future directions will need to integrate more robust climate models, better prediction tools, and innovative policy frameworks.
Conclusion
As we face the reality of climate change, it is crucial to appreciate the historical context of natural fluctuations and the profound impact of human activities. By embracing technology and international cooperation, we can hope to steer our planet towards a more sustainable future.
Further Reading and Resources
For those interested in exploring the detailed scientific analysis and research findings, please refer to the full text of the study available here and consider its broader implications as discussed in academic circles.
