Kinetic Analysis of Reafix Yellow B8G Dye Removal Using Boiler Ash
Introduction
Industrial wastewater management remains a significant challenge, particularly in the textile sector, where dyes like Reafix Yellow B8G pose environmental risks due to their persistence and harmful nature. This post explores a kinetic study that investigates the use of boiler ash, a byproduct of biomass combustion, as an efficient adsorbent for removing Reafix Yellow B8G dye from wastewater. This study highlights the potential of using waste materials for wastewater treatment, aligning with sustainable development goals and circular economy principles.
Boiler Ash: A Green Solution for Wastewater Treatment
Boiler ash, often discarded as waste, can be repurposed for environmental remediation due to its porous structure and adsorption properties. This study evaluates the adsorption kinetics of Reafix Yellow B8G dye using boiler ash under controlled conditions, demonstrating that this method offers a low-cost and eco-friendly alternative for treating dye-contaminated effluents.
Key Findings from the Kinetic Study
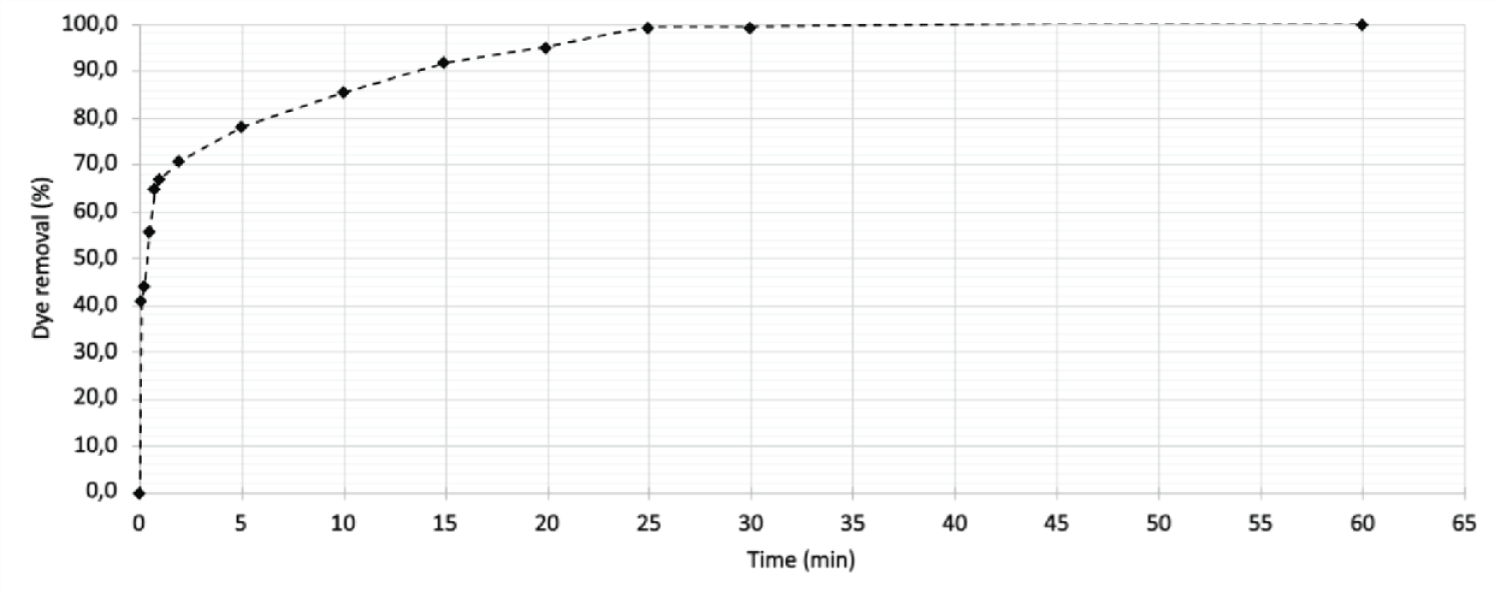
Rapid Adsorption Rates: The kinetic analysis revealed that the adsorption process is rapid, achieving 90% dye removal within the first 15 minutes. Equilibrium was reached in just 30 minutes, resulting in complete dye removal.
Efficiency of Boiler Ash: The high adsorption efficiency makes boiler ash a viable option for large-scale applications in industrial wastewater treatment. The use of this readily available byproduct contributes to cost-effective operations and minimizes the environmental impact of waste disposal.
Environmental Benefits: This approach not only addresses the problem of dye contamination in water bodies but also reduces the need for incineration or landfill disposal of boiler ash, contributing to a more sustainable and circular economy.
Applications in the Circular Economy
The use of boiler ash for dye adsorption aligns with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), specifically those aimed at responsible consumption and waste reduction. By utilizing industrial byproducts for environmental remediation, industries can reduce their ecological footprint and turn waste into a valuable resource.
Challenges and Recommendations
Although boiler ash proved effective in this study, further research is needed to understand how variations in pH, temperature, and real industrial effluents impact adsorption efficiency. Testing the method with different types of dyes and contaminants could broaden its applicability. Additionally, exploring the regeneration of used boiler ash could further enhance its economic viability.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates the potential of using boiler ash as a sustainable solution for the removal of hazardous dyes like Reafix Yellow B8G from industrial wastewater. By adopting such innovative approaches, industries can move closer to achieving environmental sustainability while complying with regulatory standards. For more details, you can access the full study here: Full Text, PDF, and DOI.
Tags: #SustainableWasteManagement #WastewaterTreatment #CircularEconomy #BoilerAsh #TextileIndustry #EnvironmentalEngineering #Adsorption #EcoFriendlySolutions #IndustrialWasteReuse #IgMinResearch