Application of Virtual Reality (VR) in Facility Management Competency-based Training (CBT) in the Era of Industrie 5.0
Revolutionizing Facility Management Training with Virtual Reality in the Era of Industrie 5.0
Facility management (FM) training has traditionally relied on lecture-based methods, often leaving staff underprepared and contributing to high turnover rates. The integration of Virtual Reality (VR) into Competency-Based Training (CBT) provides a transformative alternative. The study Application of Virtual Reality (VR) in Facility Management Competency-Based Training (CBT) in the Era of Industrie 5.0 (Full Text, DOI) highlights the potential of VR to enhance learning and align with Industrie 5.0 principles of human-machine collaboration.
The Power of VR in Facility Management
Industrie 5.0 emphasizes personalization and humanization in technology. VR aligns perfectly with this vision by providing immersive, interactive training environments. Key benefits identified in the study include:
- Enhanced Understanding and Retention: VR-based training allows learners to “walk” through virtual environments, interact with equipment, and simulate real-world scenarios, improving comprehension and memory retention.
- Increased Motivation: The interactive nature of VR fosters engagement and interest compared to traditional lecture-based methods.
- Addressing Safety Concerns: Trainees can practice tasks in high-risk areas (e.g., switch rooms) without physical danger, mitigating potential accidents.
Methodology and Results
The study involved 20 facility managers divided into two groups: one receiving traditional training and the other VR-based training. Key findings include:
- Superior Performance: Participants trained with VR scored higher in post-training quizzes.
- Positive Feedback: Surveys revealed that VR trainees rated their learning experience and competency improvement more favorably.
- Overcoming Cybersickness: While some trainees experienced dizziness, recommendations such as shorter sessions and enhanced hardware were proposed to address these challenges.
Applications in Facility Management
- Training in Restricted Areas: VR simulates hard-to-access locations like rooftops and pump rooms, allowing new hires to familiarize themselves with critical tasks.
- Emergency Response Drills: Trainees can practice fire evacuation and medical emergencies in a controlled virtual setting.
- Complex Maintenance Tasks: Interactive modules guide users through detailed maintenance procedures for electrical and HVAC systems.
Industry Impact
By incorporating VR, facility management companies can:
- Reduce Turnover: Better training leads to higher confidence and job satisfaction.
- Ensure Workforce Readiness: Trainees are better prepared for real-world challenges.
- Advance Sustainability Goals: Training on energy-efficient systems and practices becomes more effective in virtual settings.
Challenges and Future Directions
While promising, VR adoption in training requires addressing certain limitations:
- Hardware Costs: Initial investment in VR headsets and supporting infrastructure can be high.
- Cybersickness: Tailored content and optimized systems are needed to minimize discomfort.
- Scalability: Expanding VR modules across diverse FM scenarios requires significant resources.
Conclusion
VR has the potential to revolutionize facility management training by aligning with Industrie 5.0 principles and addressing traditional training gaps. With proper implementation, it can enhance safety, efficiency, and learner engagement while preparing the FM workforce for a technologically advanced future.
For more insights, read the full study (Full Text, DOI).
Tags: Virtual Reality, Facility Management, Competency-Based Training, Industrie 5.0, Workforce Training, Immersive Learning, Safety Training.
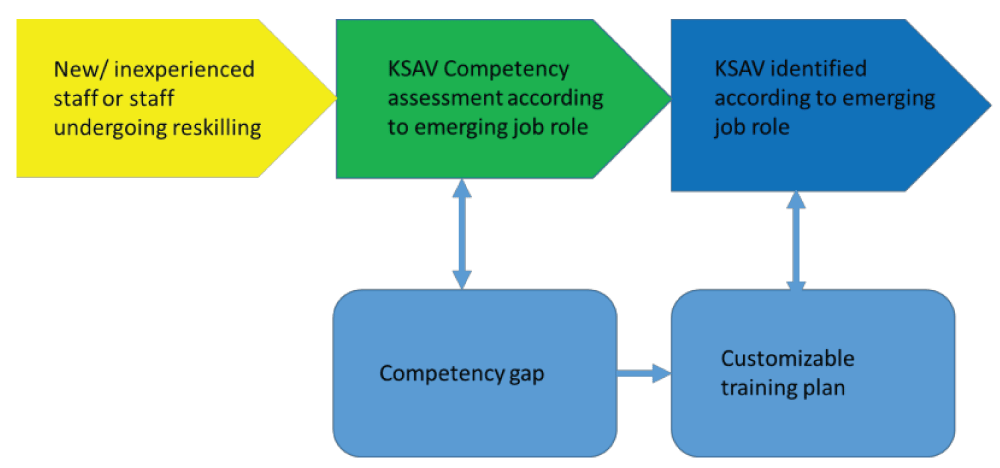
Figure 1: Competency-based training framework.

Figure 2: Screenshot of VR Training view within switch-room.
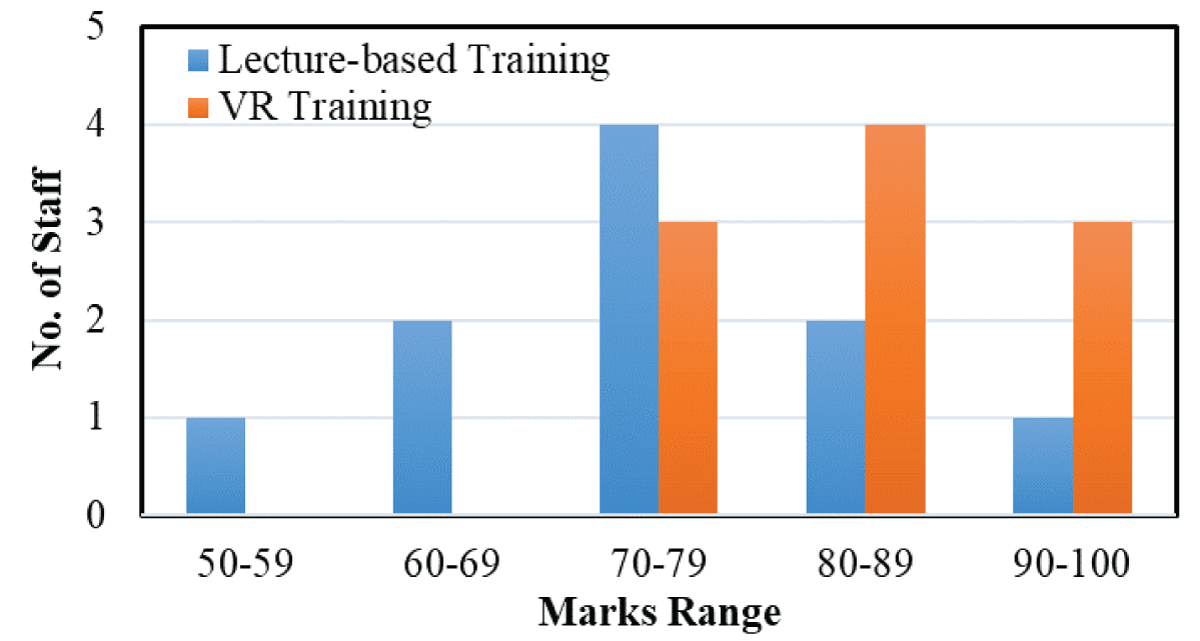
Figure 3: Results from the post-training Quiz.
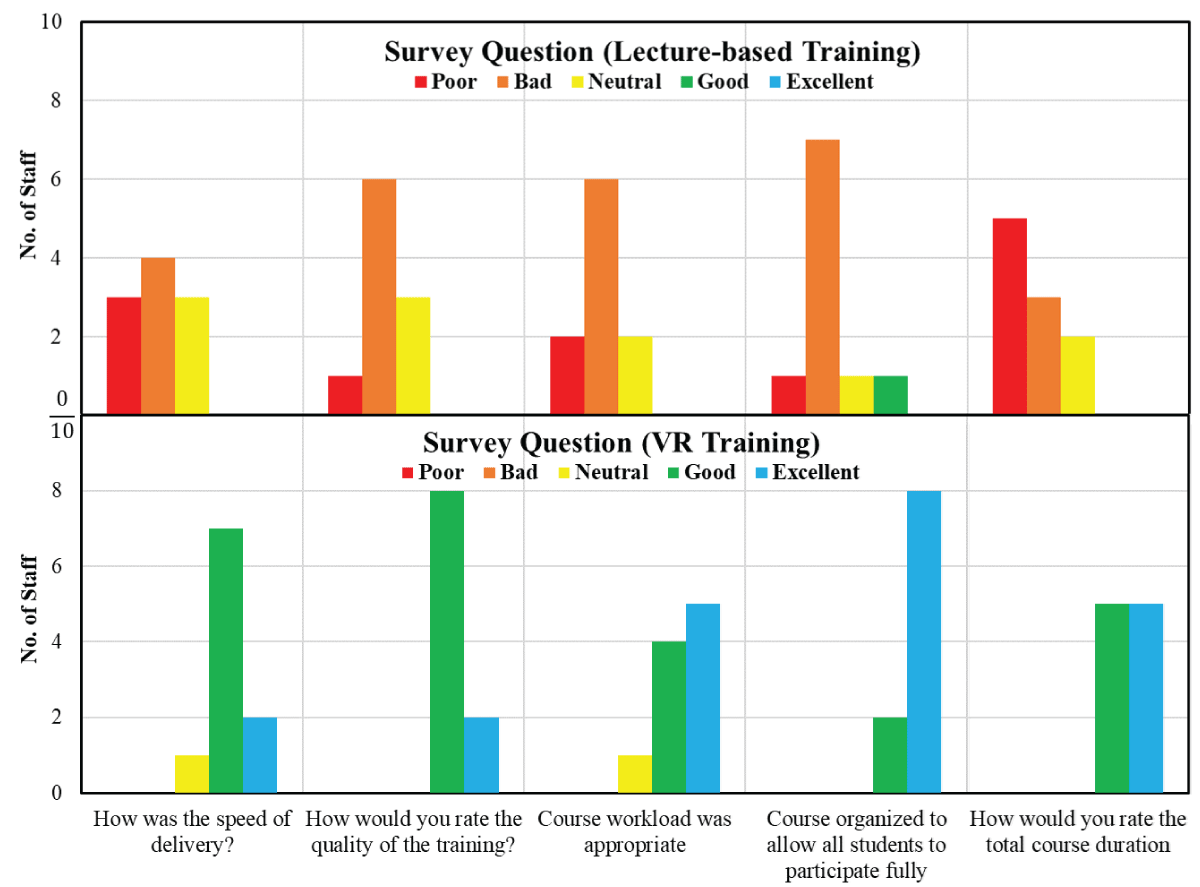
Figure 4: Results from post-training survey (training quality).
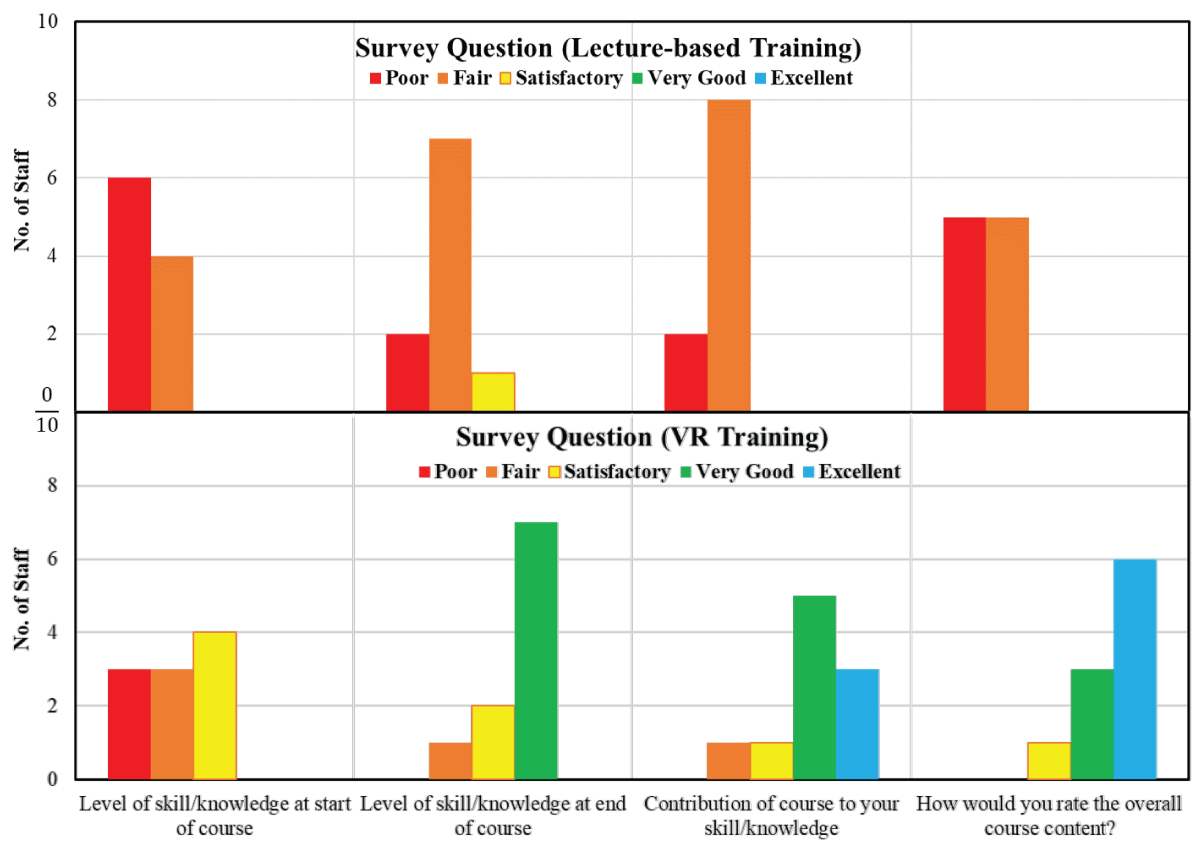
Figure 5: Results from post-training Survey (contribution of training).
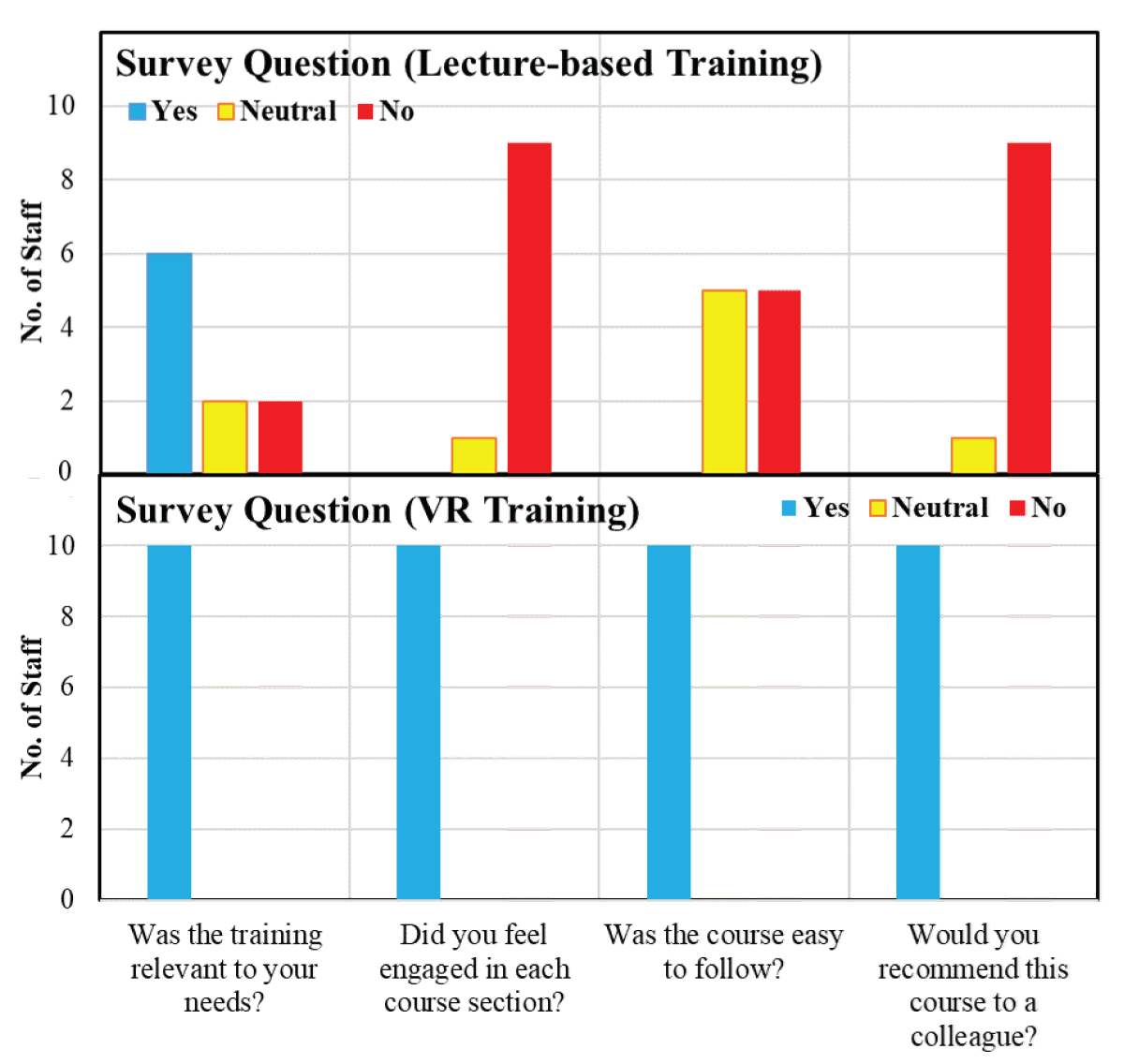
Figure 6: From post-training Survey (training feedback).
Figure 7: Study on the Built Environment Workforce in Singapore [].
