Assessment of Slip Resistance Across 10 Indoor Flooring Materials
Enhancing Indoor Safety: Slip Resistance Evaluation of 10 Indoor Floor Surfaces
Slip and fall incidents remain a significant safety concern in both residential and workplace environments, contributing to injuries, fatalities, and economic losses. Understanding the slip resistance of various flooring materials under different conditions is critical for minimizing such risks. A recent study, as detailed in IGMIN Research Article #199, sheds light on this issue by evaluating slip resistance across 10 common indoor flooring surfaces.
The Problem of Slips and Falls
Slips and falls are among the leading causes of injuries, particularly among the elderly and workplace employees. According to the National Safety Council, falls accounted for over 44,000 deaths in 2021, making them a pressing public health issue. Moreover:
- Workplace Incidents: Falls are a leading cause of workers’ compensation claims, often due to wet or uneven surfaces.
- Vulnerable Populations: Senior citizens are especially at risk, with one in four experiencing a fall annually, according to the CDC.
The primary factors contributing to slips and falls can be categorized as:
- Extrinsic Factors: Environmental conditions like wet floors, uneven surfaces, poor lighting, or improper footwear.
- Intrinsic Factors: Health-related issues such as poor balance, fatigue, or visual impairments.
Research Overview
This study aimed to assess the slip resistance (SR) of 10 indoor flooring surfaces under various conditions:
- Surface Conditions: Dry versus wet.
- Treatment Effects: Coated versus uncoated surfaces.
The researchers used the English XL Variable Incidence Tribometer (VIT) to measure the static coefficient of friction (SCOF), a standard metric for evaluating slip resistance.
Methodology
Flooring Materials
The study selected 10 common flooring samples, including ceramic tiles and laminates, obtained randomly from a flooring supplier.
Testing Procedure
- Preparation:
- Surfaces were cleaned using a citrus-based cleaner.
- Tiles were mounted on a cork base for stability.
- Conditions:
- Dry and wet surfaces were tested.
- Anti-slip coatings were applied to evaluate their impact on SR.
- Measurements:
- SR readings were taken using the English XL VIT in four directions (North, East, South, West) for each surface.
- Tests were repeated under all conditions, and data were analyzed using statistical tools like paired T-tests and ANOVA.
Key Findings
1. Impact of Wet Conditions
- Wet surfaces significantly reduced SR values compared to dry surfaces.
- For uncoated surfaces, SR readings fell below the safety threshold (SCOF < 0.50) in most cases, increasing the risk of slips.
2. Effectiveness of Anti-Slip Coatings
- The application of anti-slip coatings improved SR values, bringing wet surfaces to safe levels in most cases.
- Coated surfaces demonstrated consistent traction, regardless of dry or wet conditions.
3. Variability Among Flooring Types
- Ceramic tiles generally showed higher SR values than laminates under both dry and wet conditions.
- Variability in SR readings was observed, highlighting the importance of material-specific evaluations.
Discussion
The findings underscore the importance of proactive measures to improve walkway safety:
- Coating Application: Anti-slip treatments effectively mitigate the risk posed by wet conditions, making them a recommended intervention.
- Material Selection: Flooring materials should be chosen based on their inherent slip resistance and the environmental conditions of their intended use.
Policy Implications
- Standards like ASTM F1646 and recommendations from the National Floor Safety Institute (NFSI) advocate for a minimum SCOF of 0.50 to ensure safety. This study reinforces the need for compliance with such standards.
Practical Recommendations
To enhance indoor safety and reduce slip-related incidents, the following steps are recommended:
1. Conduct Regular Safety Assessments
- Use tools like tribometers to evaluate SR values of flooring surfaces periodically.
- Identify high-risk areas prone to wet conditions or heavy foot traffic.
2. Apply Slip-Resistant Coatings
- Treat flooring surfaces with anti-slip coatings, particularly in areas with frequent exposure to water, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and entryways.
3. Choose High-SR Materials
- Select flooring materials with high inherent slip resistance, especially in environments catering to seniors or workplaces with safety concerns.
4. Implement Preventative Measures
- Install floor mats in high-traffic areas.
- Use warning signs and barriers to highlight wet floors or other hazards.
5. Adhere to Standards
- Ensure compliance with guidelines set by organizations like ASTM, OSHA, and NFSI for walkway safety.
Future Research Directions
While this study provides valuable insights, further research is needed to:
- Evaluate additional flooring materials and coatings.
- Explore the long-term durability of anti-slip treatments under real-world conditions.
- Develop cost-effective solutions for residential and commercial applications.
Conclusion
The slip resistance of flooring surfaces plays a crucial role in preventing slips and falls. This study highlights the importance of evaluating SR under varying conditions and applying treatments to enhance safety. By adopting proactive safety measures, property owners and employers can significantly reduce the risk of slip-related injuries, protecting lives and minimizing associated costs.
Tags
- Slip Resistance
- Floor Safety
- Anti-Slip Coatings
- Indoor Flooring
- Workplace Safety
- Tribometry
- Slip and Fall Prevention
- Safety Standards
- Flooring Materials
- Static Coefficient of Friction
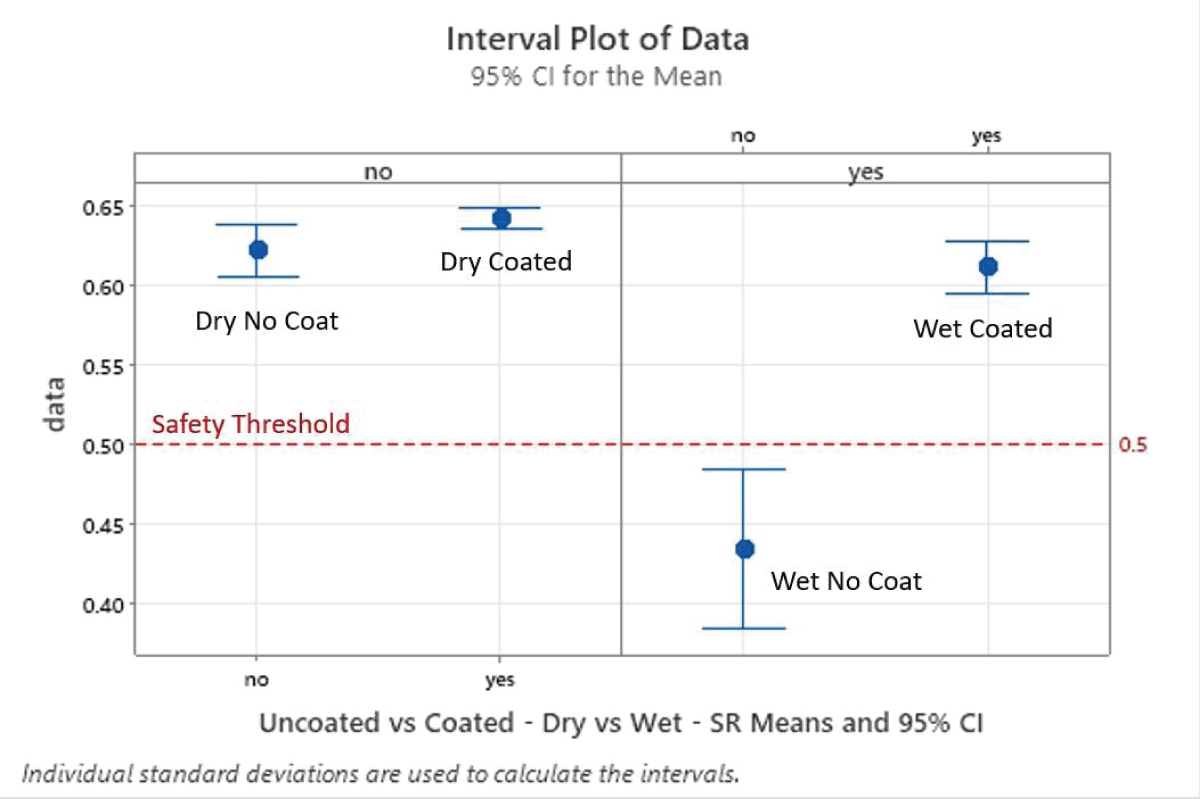
Interval Plot of Dry vs. Wet and Uncoated vs. Coated Mean SR w/95% CI. Significant Differences – p - Values < 0.05 in Uncoated Dry vs. Wet.
